Fire extinguishers are essential safety devices, but how can you be sure they’re ready to perform when needed? To guarantee their effectiveness, fire extinguishers undergo periodic testing, and one essential method employed is hydrostatic testing. In this blog post, we will delve into what hydrostatic testing is, why it’s necessary, and how it contributes to the reliability of fire extinguishers.
What is Hydrostatic Testing?
Hydrostatic testing is a method used to assess the structural integrity of pressure vessels, including fire extinguishers, by subjecting them to high-pressure water or another non-compressible fluid. This process helps ensure that the extinguisher can withstand the pressure it might encounter during an emergency without compromising its safety.
Why is Hydrostatic Testing Necessary?
- Safety Assurance: Hydrostatic testing is crucial for maintaining the safety and reliability of fire extinguishers. By subjecting them to elevated pressure levels, it helps identify any weaknesses or defects in the extinguisher’s construction.
- Compliance with Regulations: Various safety organizations, such as the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), mandate hydrostatic testing to comply with industry standards. Adhering to these regulations is essential to ensure that fire extinguishers are fit for use in emergency situations.
- Preventing Catastrophic Failures: Fire extinguishers are pressurized vessels, and failure during operation can be catastrophic. Hydrostatic testing helps prevent such failures by identifying potential issues before they become critical.
Hydrostatic Testing Process:
- Visual Examination: Before the test, a thorough visual inspection is conducted. This includes checking for dents, corrosion, or any other damage that may compromise the structural integrity of the extinguisher.
- Removal of Components: Valves, internal parts, and hose assemblies are removed before testing. Certain types of extinguishers may have specific recommendations on which internal parts should not be removed.
- Pressure Testing: The extinguisher is pressurized using water or another suitable fluid. The pressure is maintained for a minimum of 30 seconds, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of the vessel’s ability to withstand pressure.
- Gauge Calibration: Ensure that pressure gauges used in the test are calibrated, meeting accuracy standards.
- Drying Process: After the test, all components are thoroughly dried. This step is crucial to prevent corrosion and ensure the extinguisher’s longevity. When using drying equipment is should not exceed 150°F (66°C).
- Record Keeping: Maintain records of the hydrostatic test, including the date, test pressure, and the person or organization conducting the test. Labels on low-pressure cylinders include the month and year of the test, test pressure used, and details of the testing agency. High-pressure cylinders that pass the test are stamped with the retester’s identification number and the test date per DOT/TC requirements.
Frequency of Hydrostatic Testing:
Hydrostatic testing is performed at regular intervals, as outlined by industry standards. The frequency varies depending on the type of extinguisher and the materials used in its construction. For instance, extinguishers with aluminum cylinders exposed to high temperatures may require more frequent testing. The following chart provides a quick reference guide for required testing intervals.
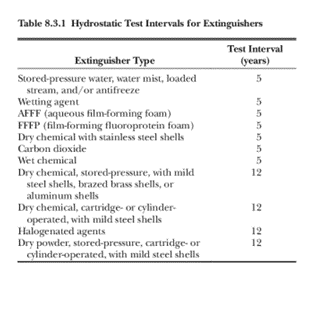

In conclusion, hydrostatic testing is a vital component of ensuring the reliability and safety of fire extinguishers. By subjecting these life-saving devices to rigorous pressure assessments, we can identify and address potential issues, ultimately contributing to their effectiveness in safeguarding lives and property during emergencies. Regular compliance with hydrostatic testing requirements ensures that fire extinguishers remain a reliable first line of defense against small fires.
